Dear Readers,
As I begin to write this blog, there are reports from different parts of the globe of Governments considering a full opening of the economic activities and removal of all restrictions. Policy makers believe that time has come for people to accept COVID-19 as a harsh reality and move on with their daily routines.
With this backdrop in mind I have tried to analyze few crisis prone industries which were affected the most after a big global crisis. I have selected these industries based on three parameters:
- Systemically important
- Vulnerability to crisis
- Long time frame to recovery
In today’s blog I focus on the first set of crisis prone Industries based on their response to past big crisis and how we could draw lessons from it to make prediction for the post Pandemic period.
1.Airline Industry Post 9/11:
The terrorist attacks on New York’s World Trade Center on September 11, 2001 struck a massive blow to the airline industry both in U.S. and around the world. If we compare it with the current pandemic, we will find some similarities. In both cases, the U.S. Government closed airports and banned flights leading to cancelling or postponing of thousands of flights. U.S. AIRWAYS and United Airlines filed for bankruptcy in the aftermath of the attacks in 2002 followed by Delta Air Lines, Northwest Airlines and Comair in 2005, and American Airlines in 2011. Several airlines bleeding with cash asked for Government Bailout. As in today, the Congress in those days passed a bipartisan bailout package to mitigate losses that came as a result of the terrorist attacks.
The NYSE Arca Airline Index closed on September 10, 2001, at $116.97 a day before the attack took 17 years to come to the same level on June 7, 2017 when the the index reached $118.12.
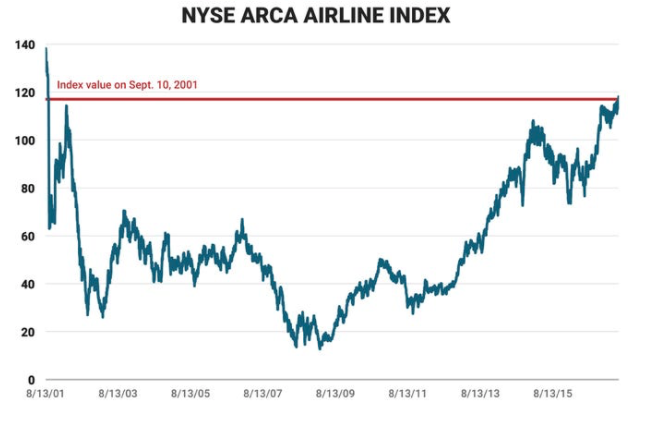
Source: Bloomberg
Consolidation in the Industry:
Prior to 9/11, nine airlines held 80 percent of the market share in U.S. During last 15 Years, rapid consolidation of the industry has resulted in four legacy carriers — Delta, United, American and Southwest — controlling nearly 80 percent of the market. The 15 mergers and acquisitions that happened during the period of 2005 to 2016 included the consolidation of some of the biggest players: US Airways, Continental and Northwest, under their legacy successors today known as American Airlines, United and Delta.
Post Pandemic Prediction :
- Short Term: Just as the 9/11 attacks brought new market leaders in aviation, the COVID-19 pandemic is likely to have a similar effect. If the past serves as a guide to the future, then we should expect layoffs and low ticket prices within the airline industry in the short run.
- Medium and Long Term: In medium to long term there could be more lasting demand-side shocks that can provoke bankruptcies, bailouts and mergers in the airline industry.
2.Technology Sector Post Dot Com Bubble:
“Dot Com Bubble” refers to the phenomenal rally in Technology stocks in the late 90s that peaked around 2000 and fizzled in 2002 . During this period investors entered the market with the hope of capitalizing on what seemed like a rare market opportunity, ignoring sky high valuations at their own peril. They were fascinated by the long term potential of the internet and invested in everything that seemed related to Technology. 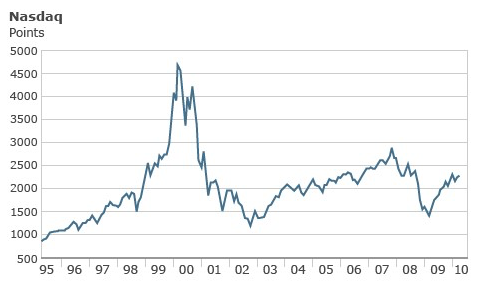
Source : Bloomberg
During this period hundreds of technology firms rushed to the public markets to get listed and ultimately fell flat when the bubble burst. The Technology IPO market never again reached those highs. It plummeted to 6 in 2008 during the Financial Crisis.

Source: J Ritter of University of Florida
Rise of Unicorns (Private Companies valued greater than $1 Billion) in the Technology Industry:
IPOs aren’t becoming less frequent because investors have stopped investing in technology companies. Rather, technology startups are increasingly turning to private sources — venture capital firms, private equity firms, and so forth — for funding instead of offering their stock to the general public. These private sources of funding have always been an important part of Silicon Valley, but in last 2 decades they’ve become the dominant way technology companies raise money. This has led to record number of Unicorns especially post 2008 crisis.

Source: CB Insights
Post Pandemic Prediction :
Unlike the earlier crisis of “Dot Com Bubble” and Financial Crisis of 2008, the current Pandemic has brought several opportunities for the Technology Industry.
Short Term : It’s likely that ‘Big Tech’ companies such as Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Facebook etc have benefited from the crisis in terms of increased consumer demand. These companies are likely to emerge stronger and more valuable, helping to sustain substantial investor interest. These companies have started acquiring and investing in newer ventures
Medium and Long Term: In the medium to long term, there will likely be more greater investor interest in the kinds of niche tech that have found their market during the COVID-19 crisis, such as the next generation of streaming and video communication, remote security, tele-medicine etc.
3.Banking and Financial Sector post 2008 Crisis:
The 2008 crisis originated from within the financial system. It arose because of excessive risk taking and leverage by Banks and other financial institutions. These institutions were encouraged by two laws which deregulated the financial system and allowed banks to invest in housing derivatives. These complicated financial products were so profitable that banks even lend them to ever-riskier borrowers. This instability was the base for the crisis which led to the collapse of big institutions such as Lehman Brothers, Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae. Bears Stearns was sold to JP Morgan and merrill lynch was acquired by Bank of America.
Congress authorized the Treasury to take over mortgage companies Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac—which cost it $187 billion at the time. On September 16, 2008, the Fed loaned $85 billion to AIG as a bailout. The Troubled Asset Relief Program led to $440 Billions in bailout sums for the banks.

Source : U.S Congressional Budget Office
Greater Regulation in the Industry:
- Dodd-Frank Act: On 21 July 2010 the US enacted the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the Dodd-Frank Act or the Act). The Act marks the greatest legislative change to US financial regulation since the explosion of financial legislations in the 1930s, during the Great Depression. The act not only increased the regulatory power of The Federal Reserve but also enhanced strict conditions on daily operations of systemically important financial institutions.
- Basel III : The third installment of the Basel Accords was developed in response to the deficiencies in financial regulation revealed by the financial crisis of 2007–08. It was intended to strengthen bank capital requirements by increasing bank liquidity and decreasing bank leverage.
Post Pandemic Prediction :
Short Term: Unlike the 2008 crisis, the Pandemic will not lead to more regulations for the Industry but would definitely push for more innovation. The Pandemic will accelerate adoption of Technology as banks struggle to find ways to deliver remote products and services. Some of the Digital Technology enablers could be:
- Solutions based on Data Analytics to identify and prepare for new risks
- Automation and Business process reengineering to ensure availability of digital banking services
- Artificial intelligence backed tools and conversational platforms to deal with surge in call volumes
- Video banking facilities
- Remote IPO roadshow with investors
Medium and Long Term: In the medium to long term the Industry could see adoption of Bitcoin cryptocurrencies, Fintech offerings etc becoming the new normal as countries push for Digital Financial Inclusion.
In the second and final part of this series I will focus on few more crisis prone Industries and analyze how they have reacted to crisis in the past and try to predict their response post COVID-19.
Stay Safe and Healthy !
One thought on “Post COVID-19 Prediction for Crisis Prone Industries – Part I”